Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) Sensor technology utilizes electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects. Unlike barcodes that require line-of-sight scanning, RFID operates wirelessly, allowing for quick and seamless data capture. Each RFID tag contains a unique identifier that can be read by a compatible reader within range.
It is a wireless identification technology that uses radio waves to transfer data from the card tag to an RFID reader and identify the object presence.
Just like the bar code technology, RFID is used to identify objects, persons, by reading the card tag. This is better than the bar code because the bar code can sometimes be damaged or unreadable.
Related Article: Interfacing RFID With Arduino

This RFID module is a 125KHz card reader mini-module which is design to read ing code from the 125KHz card tag.
Companies mainly use it to access authorized employees, attendance systems, and for personal identification.
RC522 RFID Sensor Pinout
The RC522 module typically has 8 pins: SDA, SCK, MOSI, MISO, IRQ, VCC, GND, and RST. Each pin serves a specific function in facilitating communication between the sensor and the microcontroller.
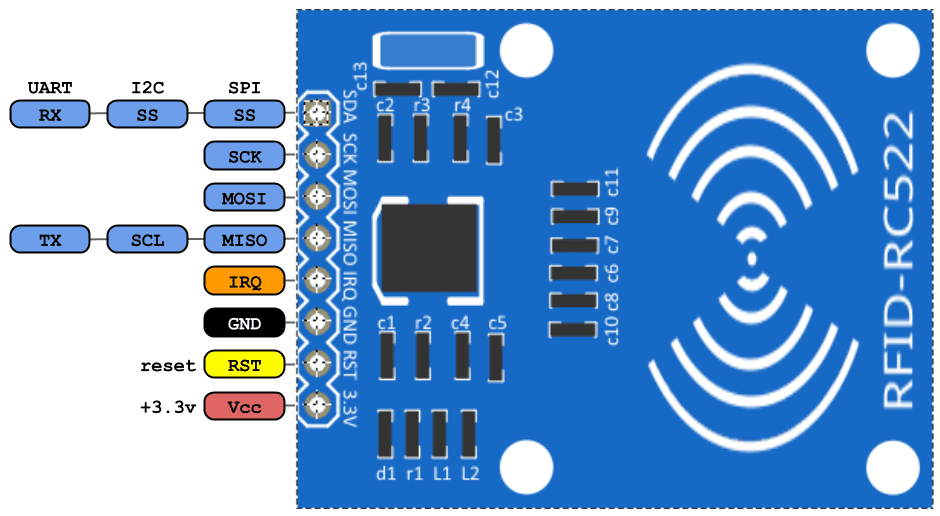
- VCC (3.3v):- VCC pin is connects to the Arduino 3.3V pin to supply power to the module. Connecting it to the 5v Arduino pin can destroy the RFID module.
- RST:- This pin is use to reset the module.
- GND:- This pin connects to the GND pin of Arduino.
- IRQ:- This is blocking or interrupt pin that can alert the microcontroller when it comes around the RFID tag.
- MISO/SCL/TX:- This pin is Master-In-Slave-Out. It acts as serial data output and connects to the Arduino RX pin.
- MOSI:- Master-Out-Slave-In pin is SPI input to the RC522 module.
- SCK:– Serial Clock is accepting clock pulses provided by Arduino.
- SS / SDA / RX:- The SDA (Serial Data) pin facilitates data transmission between the RFID module and the microcontroller. This pin usually connects to the Arduino TX pin.
Specifications of RFID Sensor
RFID sensors come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each with its own set of specifications that cater to different needs. The frequency range at which an RFID sensor operates is crucial for its performance, with options like low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high frequency (UHF) available.
The read range of an RFID sensor determines how far it can communicate with a reader device, ranging from a few centimeters up to several meters. Additionally, the data storage capacity of an RFID sensor dictates how much information it can hold and transmit during communication.
| Dimensions | 60mm × 39mm |
| Working voltage | 5V DC |
| Frequency | 125KHz |
| Read Range | Up to 3 cm |
| Max Data Transfer Rate | 10 Mbit/s |
Types of RFID Sensors Available
RFID sensors come in various types, each designed to cater to specific needs and applications. Passive RFID sensors do not need a power source and activate when they come into the vicinity of an RFID reader. Active RFID sensors have their power source, allowing them to transmit signals over longer distances with higher accuracy.
Another type is semi-passive RFID sensors which combine features of both passive and active systems, striking a balance between energy consumption and signal strength. UHF RFID sensors operate at ultra-high frequencies, enabling faster data transfer rates suitable for tracking large volumes of items simultaneously.
On the other hand, NFC (Near Field Communication) RFID sensors are commonly use for contactless payment systems or access control applications due to their short-range communication capabilities. Each type of RFID sensor offers unique benefits depending on the intended use case, making it crucial to select the right one for maximum efficiency.
Uses/Applications of RFID Sensor
- In attendance system.
- Door Looking System.
- Provide access to employees in the company.
- Home/office security systems.