Raspberry Pi is not your average fruit-inspired name; it’s a game-changer in the tech world. Imagine a credit card-sized computer that can perform like a heavyweight champ. That’s Raspberry Pi for you – compact yet mighty.
The Raspberry Pi may be a low value, credit-card sized pc that plugs into a pc monitor or TV and uses a customary keyboard and mouse.
It is a capable very little device that allows individuals of all ages to explore computing, and to be told a way to how to program in languages like Scratch and Python.
This device is capable of doing everything which we can do from a PC, from browsing the net and enjoying the high-definition video, to creating spreadsheets, word-processing, and enjoying games.
The Raspberry Pi, developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation (registration number 1129409), is a notable example.
It is a series of small single-board computers.
This device is developed to promote the teaching of basic computer science in colleges and in developing countries.
The original model became way more widespread than anticipated, selling outside its target market for uses such as robotics.
It doesn’t have to embody peripherals (such as keyboards, mice and cases). But, some accessories are included in many official and unofficial bundles.

The Evolution of Raspberry Pi Models
The Raspberry Pi has come a long way since its inception in 2012. The first model, the Raspberry Pi 1 Model B, was a game-changer with its compact size and impressive capabilities.
Over the years, the Raspberry Pi Foundation has continued to innovate, releasing newer models with enhanced features and improved performance.
With upgrades like increased processing power, more RAM, and support for dual displays, each new model offers users even more possibilities for their projects.
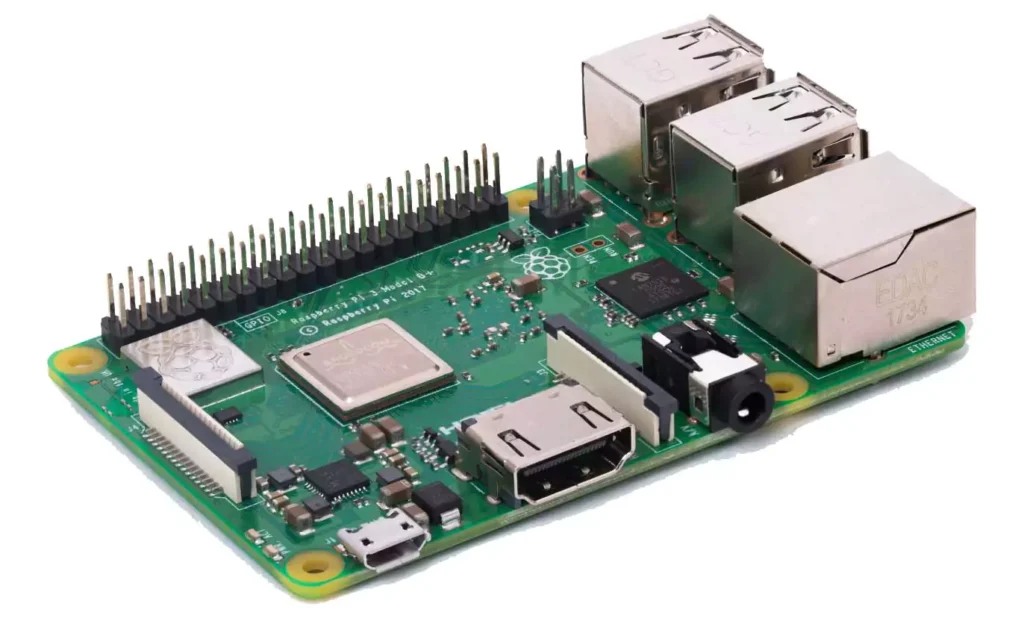
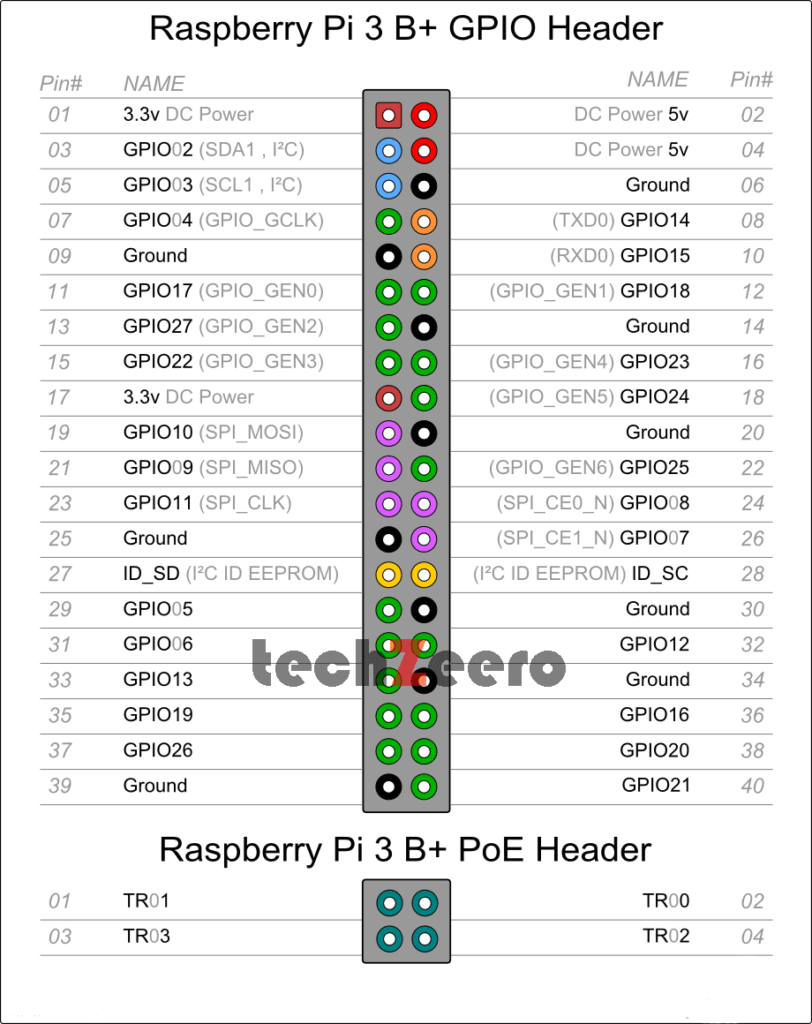
Raspberry 3 B+ Pinout
Each model of Raspberry Pi comes with its own set of pins and technical specifications that determine its capabilities.
For example, the Raspberry Pi 4 features a Broadcom BCM2711 processor, up to 8GB of RAM, multiple USB ports, HDMI output, Ethernet connectivity, and support for dual displays. This powerhouse enables users to run complex applications and multitask seamlessly.
However, older models, such as the Raspberry Pi Zero, are ideal for little projects or when space is at a premium, even though they may have fewer connections and less computing capability.
Specifications of Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+
- Broadcom BCM2837B0, Cortex-A53 (ARMv8) 64-bit SoC @ 1.4GHz.
- 1GB LPDDR2 SDRAM.
- 2.4GHz and 5GHz IEEE 802.11.b/g/n/ac wireless LAN, Bluetooth 4.2, BLE.
- The Extended 40-pin GPIO header.
- Full-size HDMI.
- 4 USB 2.0 ports.
- CSI camera port for connecting a camera.
- DSI display port for connecting a Pi touchscreen display.
- 4-pole stereo output and composite video port.
- Micro SD port for loading your operating system and storing data.
- 5V/2.5A DC power input.
- Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) support (requires separate PoE HAT).
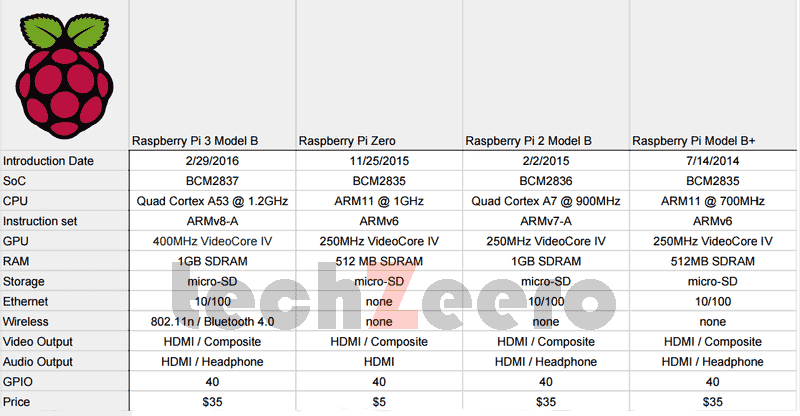
Specifications of Old Models
Common Uses for Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi is a versatile mini-computer that can be used for various projects. One common use is setting up a home media center, allowing you to stream movies, music, and videos on your TV. You can also use it as a retro gaming console by installing emulators and playing classic games from the past.
Another popular application is to creating a smart home system. With the right sensors and programming, you can automate tasks like turning lights on and off or monitoring your home security remotely. Additionally, it can be used in education to teach coding skills to students through fun and interactive projects.
Tips and Tricks for Building Projects
Looking to take your Raspberry Pi projects to the next level? Here are some tips and tricks to help you build like a pro.
- Plan Ahead: Before diving into your project, make sure you have a clear plan in place. This will help you stay organized and focused throughout the build.
- Explore Tutorials: Take advantage of online tutorials and guides available for projects. They can offer valuable insights and inspiration for your own creations.
- Experiment with Different Components: Don’t be afraid to mix and match different components to see what works best for your project. It’s all about finding the right combination.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest software updates and innovations in the Raspberry Pi community. This will ensure that your projects are always cutting-edge.
- Join Forums and Communities: Engage with other enthusiasts in forums or online communities…