The Soil Moisture Sensor is used to measure the water content (volumetric water content) of soil. This makes it ideal for performing experiments in courses such as soil science, agriculture science, environmental science, horticulture, botany, and biology. Use the soil Moisture sensor to:
- The sensor measures the loss of moisture over time due to evaporation and plant uptake.
- It can evaluate optimum soil moisture content for various species of plants.
- It is used to monitor soil moisture content to control irrigation in greenhouses.
- They can enhance your bottle biology experiments.
Related Article: Soil Moisture Sensor With Arduino
What is Volumetric Water Content?
In very simplified terms, dry soil is made up of solid material and air pockets, called pore spaces (the pore space of soil contains the liquid and gas phases of soil). A typical volumetric ratio of soil would be 55% solid material and 45% pore space.
As water is add to the dry soil, the pore spaces begin to fill with water. Soil that seems damp to the touch might now have 55% minerals, 35% pore space and 10% water. So this would be an example of 10% volumetric water content.
In this case, the maximum water content will be 45% since at that point, all of the pore space will have been completely occupied by water. Because this soil can no longer hold water at its 45% volumetric water content, it is refers to as saturated (completely wet).
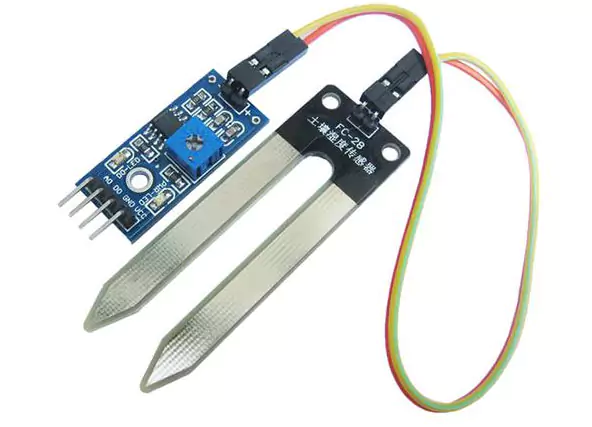
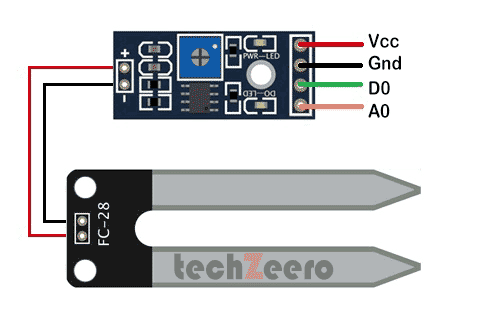
Soil Moisture Sensor Pinout
Usually, a basic soil moisture sensor will have three pins – VCC (power supply), GND (ground), and OUT (signal output). The VCC pin is where you connect the power source to provide energy for the sensor to operate. The GND pin serves as the reference point for electrical circuits by connecting them to ground.
The OUT pins are crucial as it provides analog or digital signals based on the moisture level detected in the soil.
Specifications
The specifications of a soil moisture sensor play a crucial role in determining its effectiveness in monitoring the water content of the soil. These sensors typically operate within a specific voltage range, most commonly around 3.3V to 5V.
Moreover, the sensor’s output signal is often digital, providing easy integration with different IoT devices for real-time data transmission and analysis. The measurement accuracy of these sensors can vary depending on the model, with some offering precise readings within a specific moisture range.
Many soil moisture sensors also have waterproof casings that shield the internal components from damage and corrosion, making them resistant to harsh environmental conditions.
| Board Size | 3.2 cm x 1.4 cm |
| Working voltage | 5V DC |
| Working current | <20 mA |
| Interface type | Analog |
| Working Temperature | 10°C~30°C |
How the Soil Moisture Sensor Works
This Sensor uses capacitance to measure dielectric permittivity of the surrounding medium. In soil, the dielectric permittivity is a function of the water content.
The sensor creates a voltage proportional to dielectric permittivity, and therefore the water content of the soil. The Soil Moisture Sensor averages the water content over the entire length of the sensor.
The influence zone is of 2cm with respect to the flat surface of the sensor and at extreme edges, it has little or no sensitivity.
The Soil Moisture Sensor is used to monitor soil moisture content to control irrigation in greenhouses, measure the amount of moisture lost in the soil over time due to evaporation and plant uptake (water used by plants), and assess ideal soil moisture contents for different species of plants.